Services
Our Cardiac Services
We offer safe, precise, and patient-focused cardiac services.

Electrocardiogram (ECG)
A test to record heart’s electrical activity. Quick, painless, 10-15 mins using chest patches.
The electrical activity of your heart is measured by a common, non-invasive test called an electrocardiogram, or ....
KNOW MORE
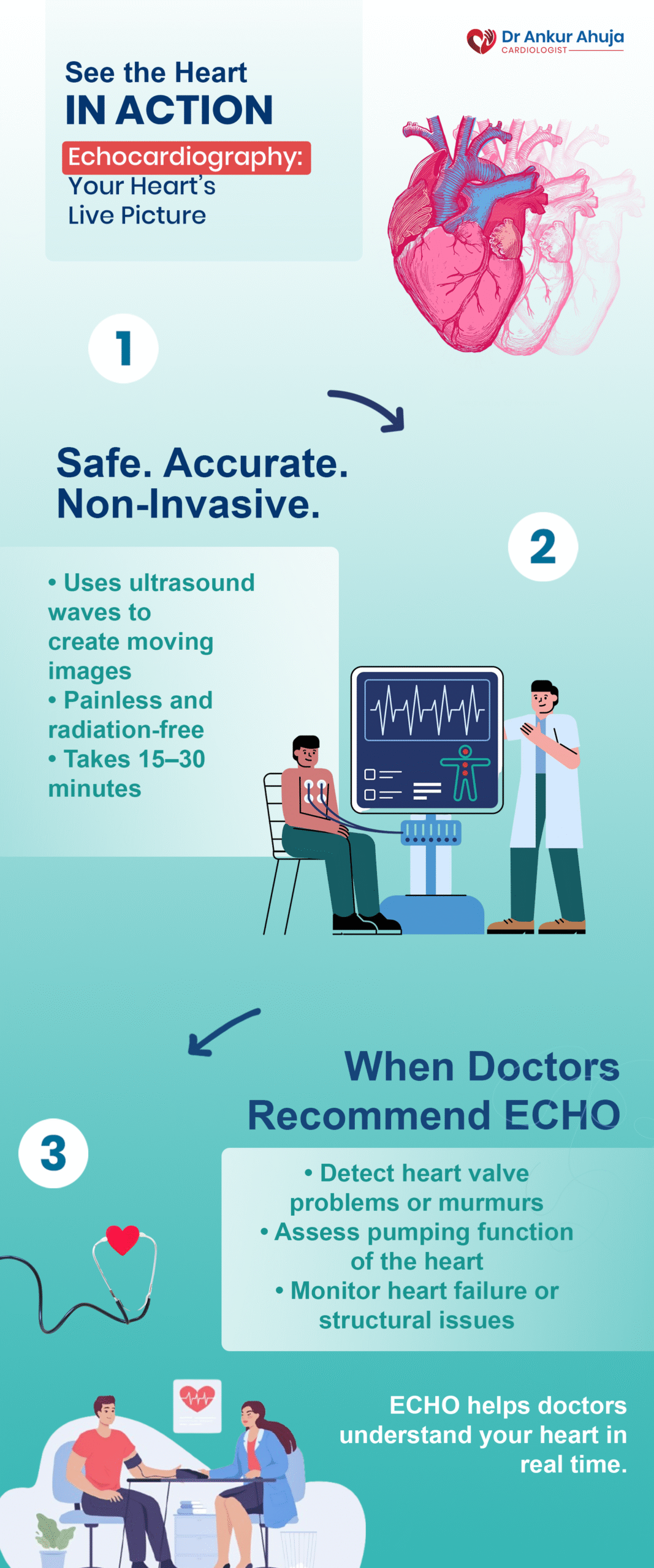
Echocardiogram
A test to check heart pumping and valves. Ultrasound probe on chest, safe, 10-15 mins.
An echocardiogram, or "echo," is a type of ultrasound in which images of your heart are produced using sound waves. It gives you....
KNOW MORE
Holter / Extended Loop Recorder (ELR)
A test to record heart rhythm for 24–48 hrs. Wear portable device, keep symptom diary.
For 24 to 48 hours, a tiny, portable device called a Holter monitor continuously records the electrical activity of your heart. It's frequently used to....
KNOW MORE
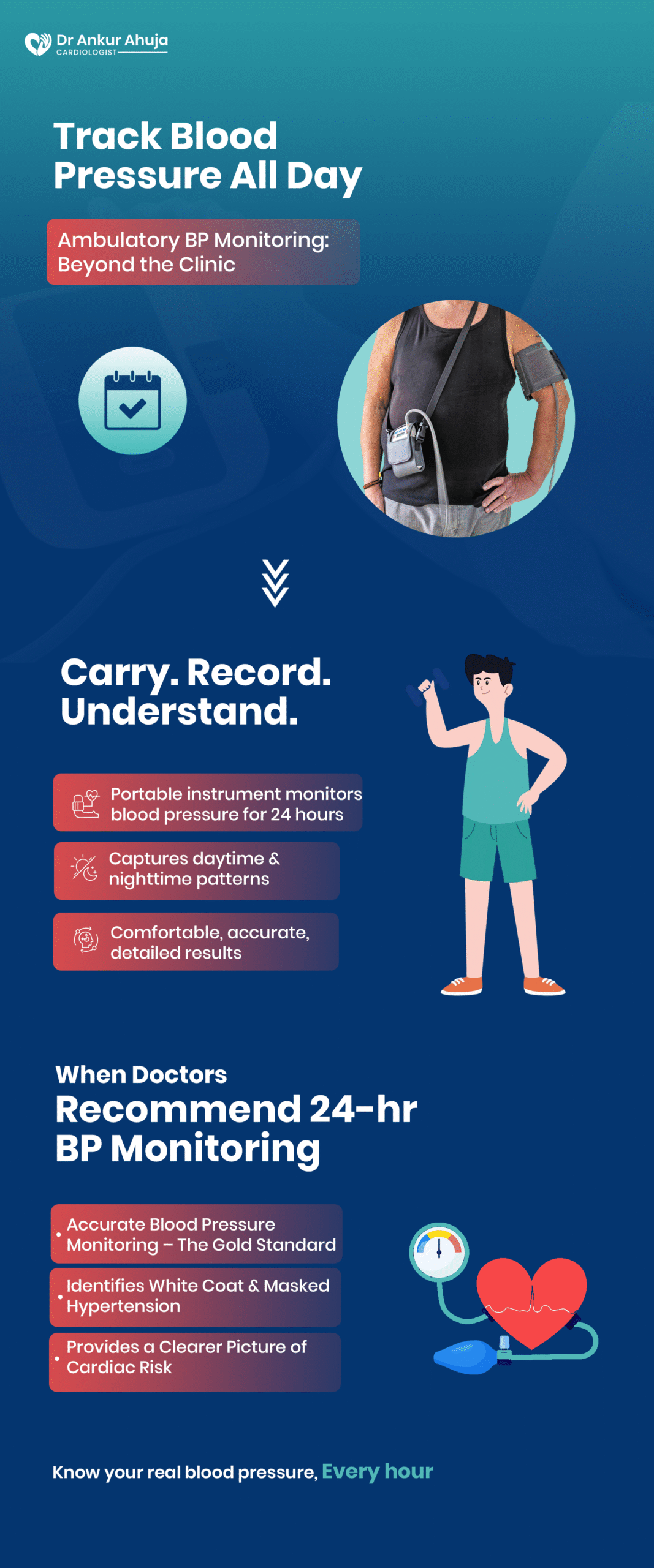
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM)
A test to track blood pressure all day & night. Cuff measures every few minutes.
By automatically taking readings throughout the day and night, the Ambulatory Blood Pressure....
KNOW MORE
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging(MPI)/ Stress Nuclear Scan
A test to study blood flow to heart muscle. Tracer shows areas with poor supply.
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging evaluates blood flow to the heart muscle during rest and stress....
KNOW MORE
Myocardial Viability PET Scan
A test to see which heart muscle can recover. Guides treatment planning.
A PET scan for myocardial viability helps identify living heart muscle that may benefit from treatment....
KNOW MORE
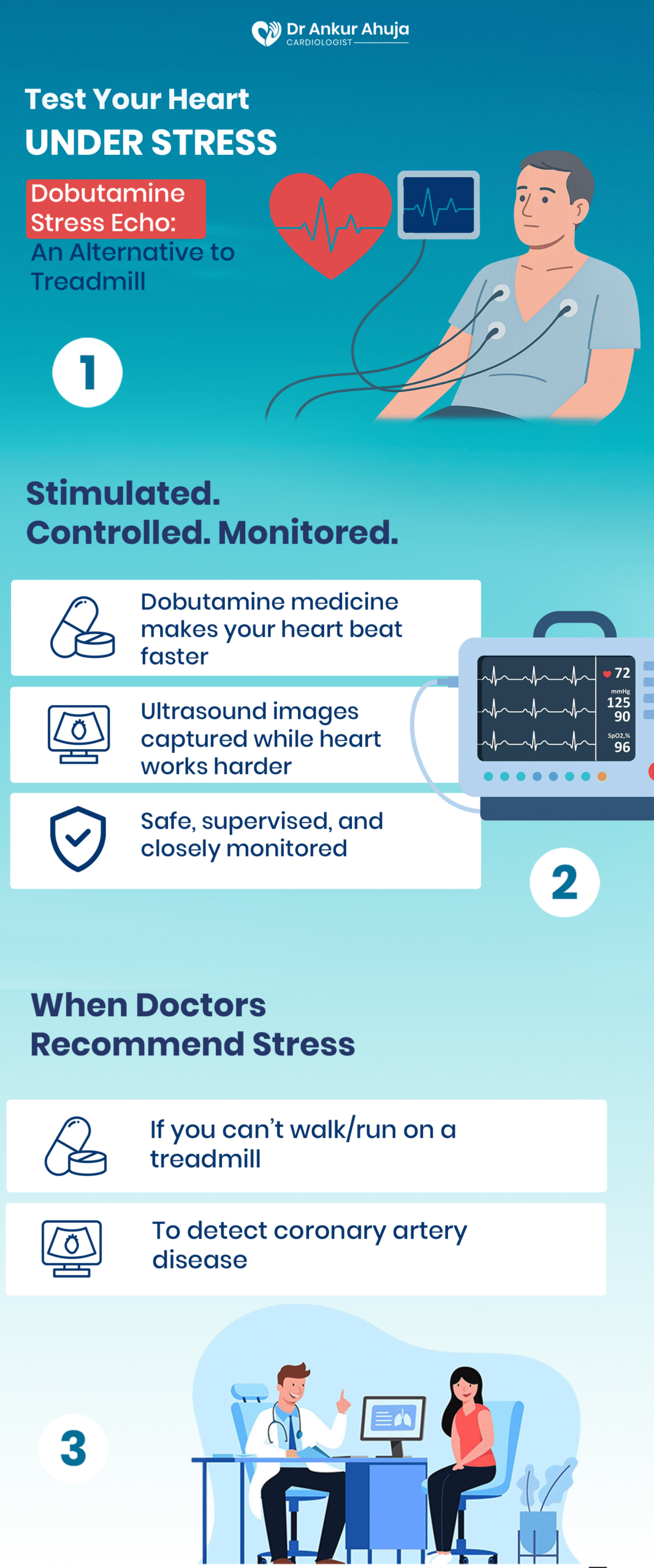
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram
A test to see heart under stress without exercise. Medicine speeds heart, echo monitors.
The Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram is a test that simulates exercise effects on your heart without requiring physical activity. This test is....
KNOW MORE
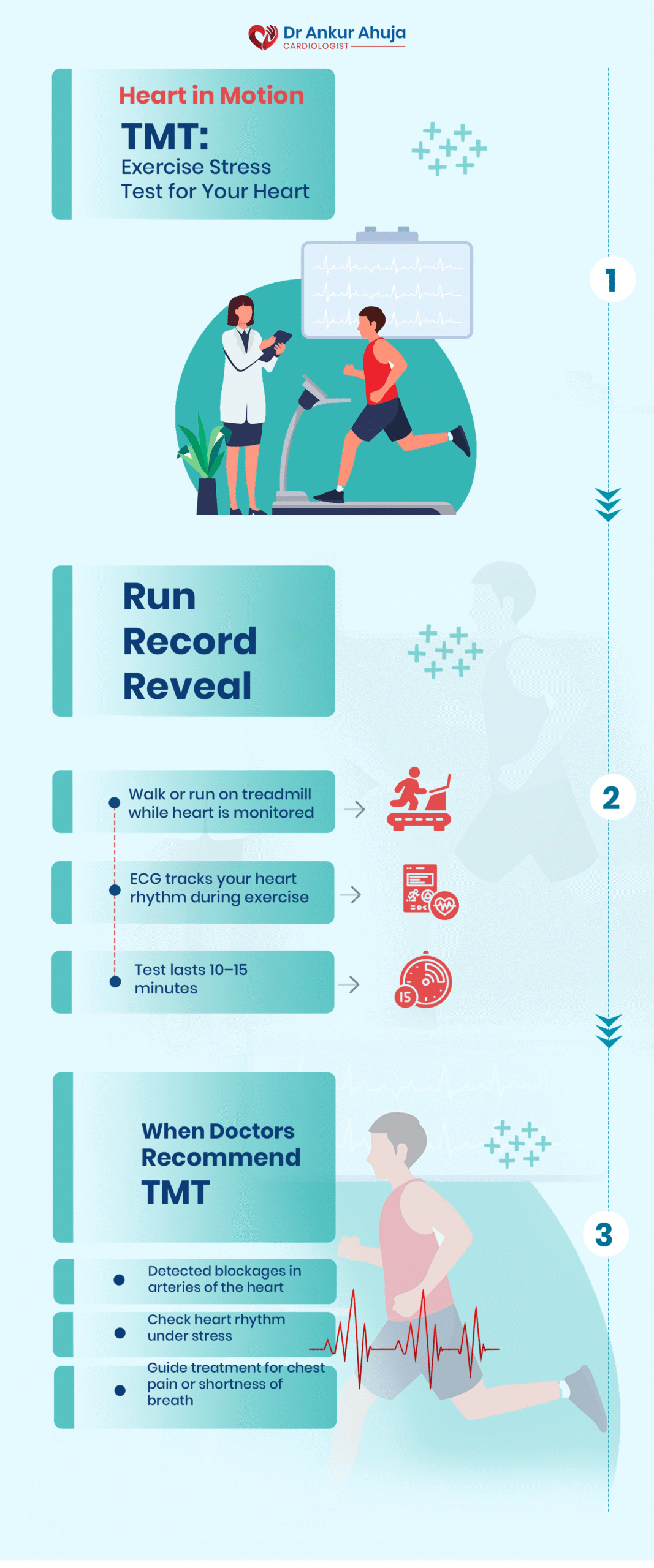
The Treadmill Stress Test (TMT)
A test to study heart response to exercise. Walk on treadmill, ECG & BP monitored.
One of the most popular ways to assess how well your heart functions while exercising is....
KNOW MORE
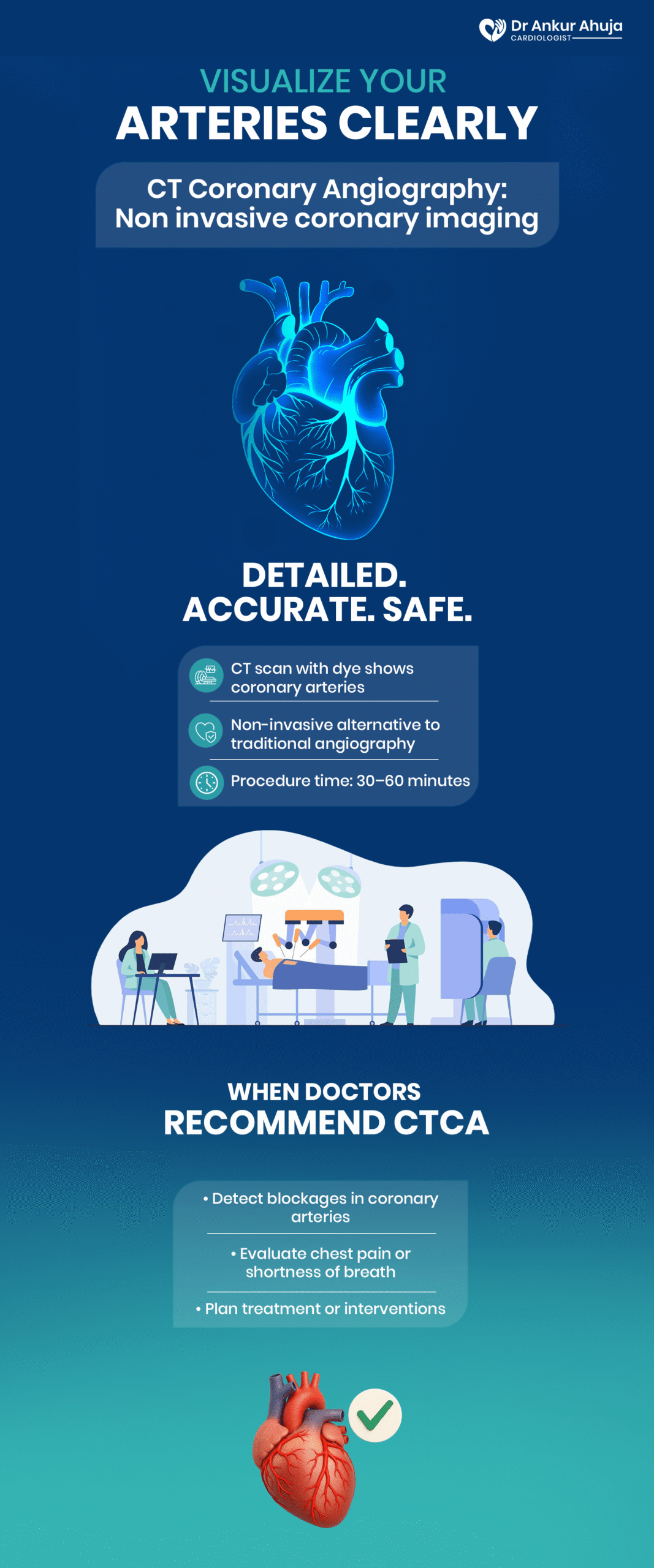
Coronary Angiography by CT (CT-CA)
A test to study artery blockages. Special dye + CT scan, 15–20 mins, fasting needed.
With the use of a CT scanner and contrast dye, a non-invasive imaging procedure called a CT Coronary Angiography (CT-CA) offers a....
KNOW MORE
Rotational Atherectomy or Rotablation
A procedure to remove hard calcium plaque. Tiny high-speed drill widens artery.
When calcified plaque, or hardened calcium, is obstructing the arteries, rotablation is a technique....
KNOW MORE
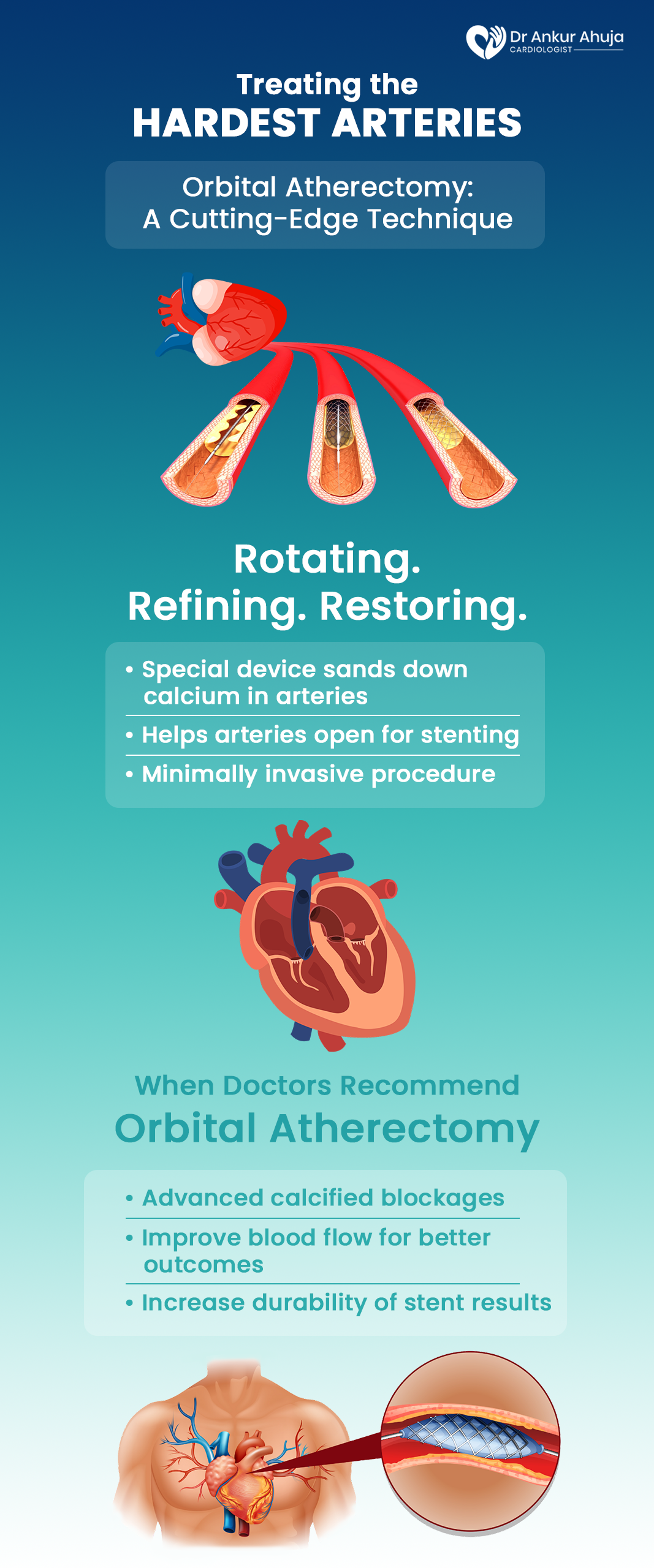
Orbital Atherectomy
A procedure to smooth calcium in arteries. Diamond-coated tool removes stubborn deposits.
Another specialized procedure used during angioplasty to treat calcified artery blockages is orbital atherectomy. Although.....
KNOW MORE
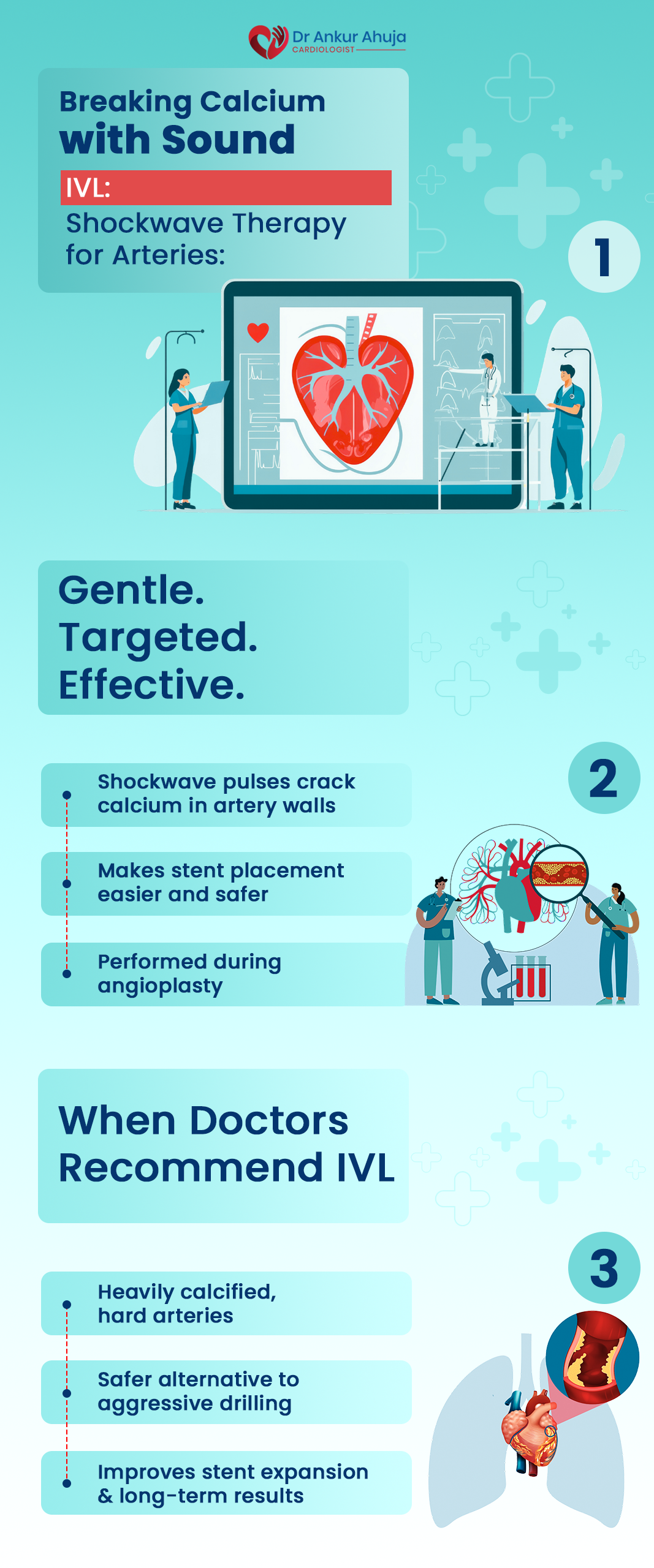
Lithotripsy Intravascular (IVL)
A procedure to crack calcium in arteries. Shockwaves ease stent placement.
A novel treatment for severely calcified coronary arteries, where balloon angioplasty or....
KNOW MORE
Intravascular Imaging : IVUS & OCT
A test to see inside arteries. Mini cameras guide stent placement with high detail.
Imaging techniques like intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) are used to....
KNOW MORE
Implantation of Pacemakers
A procedure to maintain steady heartbeat. Small device under skin fixes slow/irregular rhythms.
A pacemaker is a tiny gadget that is inserted into your body to control a sluggish or erratic heartbeat. It is frequently .....
KNOW MORE
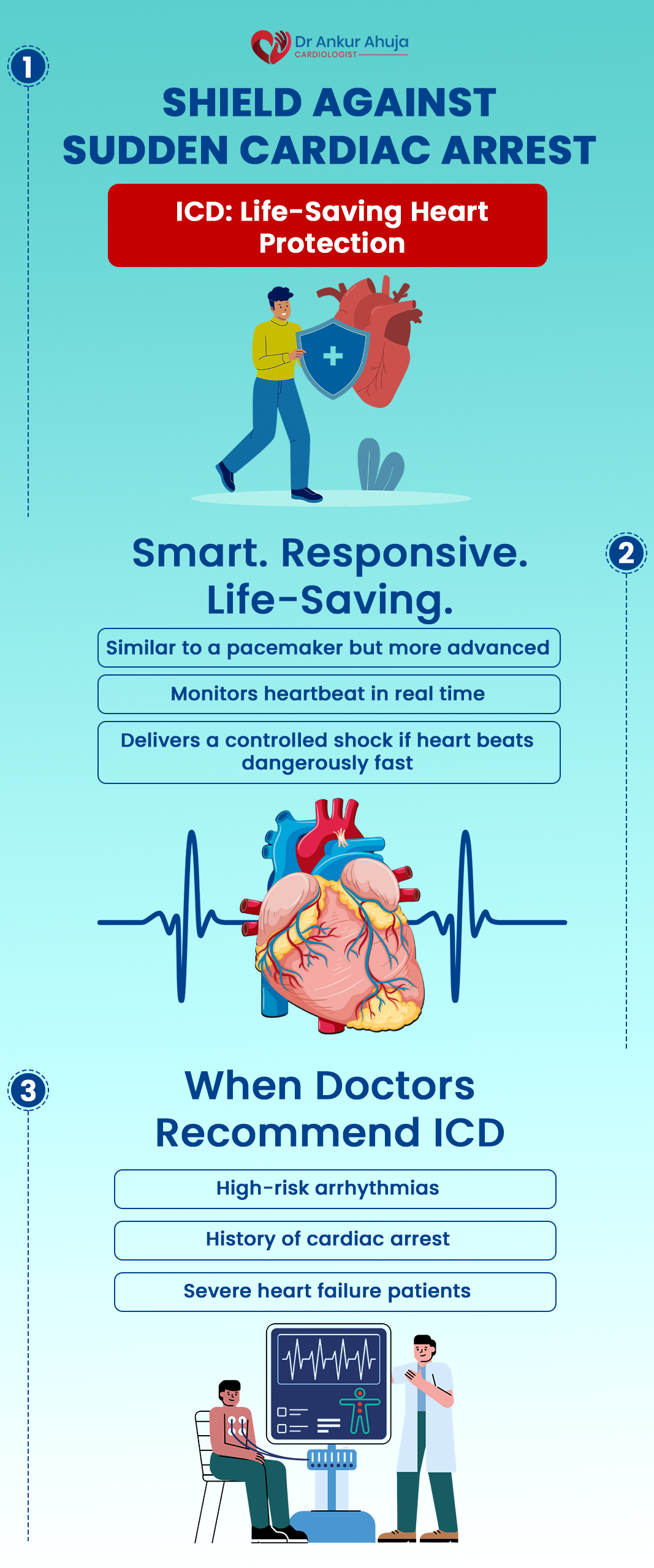
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
A procedure to protect against dangerously fast rhythms. Can deliver life-saving shock.
Similar to a pacemaker, an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) shocks the heart if it begins to beat....
KNOW MORE
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT-P/CRT-D)
A procedure to sync both sides of the heart. Improves weak pumping in severe heart failure.
People with severe heart failure, in which the left and right sides of the heart do not beat in unison....
KNOW MORE
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
A procedure to replace a damaged valve without open surgery. Delivered via small groin cut.
A damaged or narrowed aortic valve in the heart can be replaced with TAVR, a minimally invasive .....
KNOW MORE
Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair (EVAR/TEVAR)
A procedure to repair aortic bulges. Stent graft inserted via small incision, no open surgery.
The large artery that transports blood from the heart to the rest of the body, the aorta, has....
KNOW MORE
Calcium Score on CT
A test to detect calcium in heart arteries. Quick, painless CT scan.
A CT Calcium Score measures the amount of calcium in coronary arteries to assess early heart disease....
KNOW MORE
Angioplasty (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, PCI)
A procedure to open blocked arteries using balloon and stent.
Angioplasty restores blood flow to the heart by opening narrowed or blocked coronary arteries....
KNOW MORESTANDING WITH YOU, ALWAYS